Elon Musk’s tweet (“@elonmusk – Tesla press conf at 9am on Thurs. About to end range anxiety … via OTA software update. Affects entire Model S fleet. March 15, 2015“) to end “range anxiety” which has since been deleted, had me thinking not about the disappointing announcements regarding the 6.2 software patches, but about when the last time was that I’ve actually experienced range anxiety.
I must admit that it’s been a while for me. We decided to move to Tesla Motors electric vehicles because we didn’t want to have to worry about range. Both the Model S and Roadster have a range of at least 170 miles. As for recharging, using DC Charging, the Model S can Supercharge at over 300 miles per hour or quick charge using CHAdeMO over 130 miles per hour. Over AC charging, our Model S can go up to 80A (or approximately 58-62 miles per hour) and the Roadster can go up to 70A (or approximately 56 miles per hour). That’s plenty fast recharging. Besides, if you charge overnight, it’s time you’re spending sleeping anyway.
When we first started our adventure with electric vehicles with the Active E, range anxiety was a byproduct of moving from a nearly limitless range to one where each full charge lasted 80-100 miles. However, it wasn’t long that I was making the statement that the range of the Active E was limitless, as long as you can get charge and have the time to wait for a charge. If a charger was available, I plugged in, even at 110V when no L2 was available.
It was not uncommon for me to do 140 mile days in the Active E. It required charging at multiple places, but L2 at 6.6 kW and later at 5.2 kW is not exactly speedy, but it isn’t slow either, at least at the time. Now that I’m used to Supercharging, quick charging, 40 Amp/10kW charging over a NEMA 14-50 or 6-50 connector, it seems that approximately 20 miles per hour seems so slow. Public charging in 2012 was fairly plentiful and easy to use in Southern California. Rarely did I have to wait, and most of the places that I found to charge at Level 2 were relatively free. Things became relatively harder at 2013. One could say that projecting the pending difficulty in obtaining public charging with shorter range electric vehicles definitely helped contribute to the decision to get Tesla Motors vehicles.
So, Range Anxiety with the Model S? Not really. One of the first things that I did when we first got our Model S and Roadster were to get some of the available charging adapters. Aside from J1772, we got adapters for NEMA 6-50 as well as NEMA 14-50. so that we could charge the car at up to 40A. Though the Model S (with dual chargers) and Roadster can go to 80A and 70A J1772 if presented with that speed. Plus, as I recently wrote, I just got CHAdeMO for our Model S, that’s a really respectable 130 miles per hour.
Which brings me to hyper-miling and Elon’s announcement.
Hyper-miling is a skill that I learned about and learned to do when I first got the Active E. Getting the most miles per kWh was the goal (or consuming the least wH per mile as is the measure on the Model S, which I’ve measured at 307 wH per mile recently). In a nutshell, hyper-miling involves driving at a constant speed, or motor use and using larger vehicles, trucks, etc. ahead of you to lower the wind resistance that impacts your vehicle. With the Active E and the size of the 1-series that it was adapted from, it was relatively easy to find vehicles that are “larger” than it to “drift” behind and it was noticeable to see the miles per kWh climb. I’ve even hit a respectable 5.0 kWh (200 Wh per mile) on the Active E, as heavy as it is.
My most recent trip to San Diego from Los Angeles County gave me a long time to ponder this thought and put a few things to test with the Model S. Since moving to the Model S, I really haven’t given hyper-miling any further thought. Until now.
As more Model S roll off the factory floor in 2015 with Adaptive Cruise Control or Autopilot, I’ve been intrigued with the ability to set the number of car-lengths to the vehicle ahead of you (pictured below from a loaner I had driven a few weeks ago.) Figuring that such a feature really lends itself to hyper-miling.
However, a more fundamental question presented itself to me. Can I even hyper-mile a Model S? So, during this same trip to San Diego, I followed a smaller delivery truck that was the ideal candidate for my test.
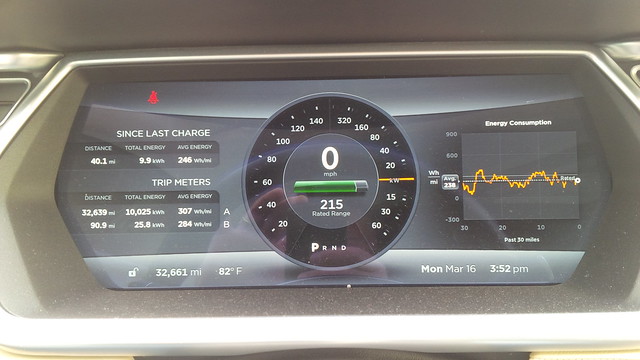
I started the drive making note of my average 30 mile consumption that is constantly graphed on my dash (as a preference that I’ve set.) See the example below.
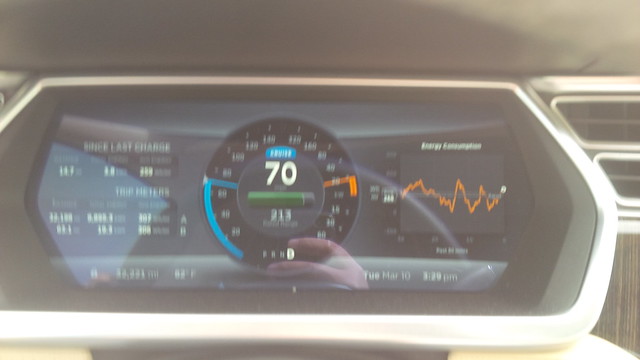
After getting my base (which, I did not record on photographs) I was in flowing traffic of around 75 mph at this point.
I decided to see what the effect was if I implememented hyper-miling techniques behind smaller vehicles. As predicted, it didn’t really help much. Too much of the wind resistance was not cut-down by the smaller vehicles.
Which leads me to try the test with the aforementioned small truck. I decided to pace the vehicle for about five miles and my average Wh per mile consumption during that period dropped at least 20 Wh per mile at a driving speed that was constant with the speed I was following smaller vehicles with. Is that a lot? Well, every bit counts and this was for five miles.
Physics doesn’t change, it’s just more difficult to find candidate vehicles to drift behind in a Model S. Next time, I’ll see if I can recreate the test using a loaner with Adaptive Cruise Control to see if I’m better than or if the Autopilot is at trying to hyper-mile. Granted, I have yet to set ACC at less than 2 car lengths for any distance, but that’s what I’ll have to do.
Oh and Range Anxiety, not really… I did that San Diego trip and back (220 miles RT) with no anxiety.